FileReader is a class in the java.io package which can be used to read a stream of characters from the files. This class uses either specified charset or the platform’s default charset for decoding from bytes to characters.
Charset: The Charset class is used to define methods for producing encoders and decoders and for recovering several names combined with the charset.
Default Charset: The default charset is defined during implicit computer start-up and it depends on the locale and charset of the underlying operating system.
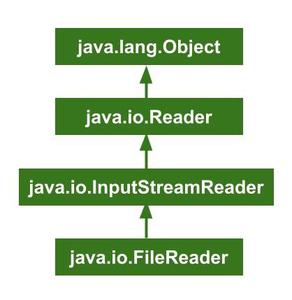
The following image shows the Hierarchical Flow of FileReader class.
Constructors
The Constructors inside FileReader are shown in the table below.
| Constructor | Description |
| FileReader(File file) | Creates a new FileReader with given File to read (using default charset) |
| FileReader(FileDescriptor fd) | Creates a new FileReader with given FileDescriptor to read (using default charset) |
| FileReader(File file, Charset charset) | Creates a new FileReader with given File to read (using given charset) |
| FileReader(String filename) | Creates a new FileReader with given FileName to read (using default charset) |
| FileReader(String filename, Charset charset) | Creates a new FileReader with given File to read (using given charset) |
Methods
The methods under FileReader are shown in the table below.
◉ read(): The read() method reads and passes a single character or -1 if the stream is ended.
◉ read(char[] charBuffer, int offset, int length): It reads a stream of characters and stores them in the given Character Buffer. Offset is the position at which it starts reading and Length is the total number of characters to be read. It passes plenty of characters read or -1 if the stream is ended.
◉ ready(): It tells whether the stream is ready to be read. A stream is said to be ready if its input buffer is not blank or empty.
◉ getEncoding(): The getEncoding() is used to return the title of the character encoding which is being used by the stream.
◉ close(): It closes the stream and releases the system resources associated with it.
// Java program to show the usage of
// IO FileReader Class
import java.io.*;
class OJC {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try {
FileReader fileReader
= new FileReader("ojc.txt");
System.out.println("Reading char by char : \n");
int i;
while ((i = fileReader.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char)i);
}
System.out.println("Reading using array : \n");
char[] charArray = new char[10];
fileReader.read(charArray);
System.out.print(charArray);
fileReader.close();
System.out.println("FileReader closed!");
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
Output:
Reading char by char :
OracleJavaCertified
Reading using array :
OracleJavaCertified
FileReader closed!
Source: geeksforgeeks.org




0 comments:
Post a Comment