Java language is one of the most popular languages among all programming languages. There are several advantages of using the java programming language, whether for security purposes or building large distribution projects. One of the advantages of using JAVA is that Java tries to connect every concept in the language to the real world with the help of the concepts of classes etc, and every class in Java has its own methods, either inherited methods or user-defined methods that are used to define the behavior of the class. In this article, we will discuss different types of methods and ways to call them.
Types of Methods:
1. User-Defined Methods: These are the methods implemented by the user in the particular class to perform a particular operation.
2. Abstract Methods: These are the methods that do not contain the body of the method and implements inside the abstract class.
3. Predefined Methods: These are the methods that are predefined and available in the java library to perform operations, for eg the hashcode() method.
4. static Methods: These are methods that are accessible without any instance of the class. The memory management of these methods is different from ordinary methods.
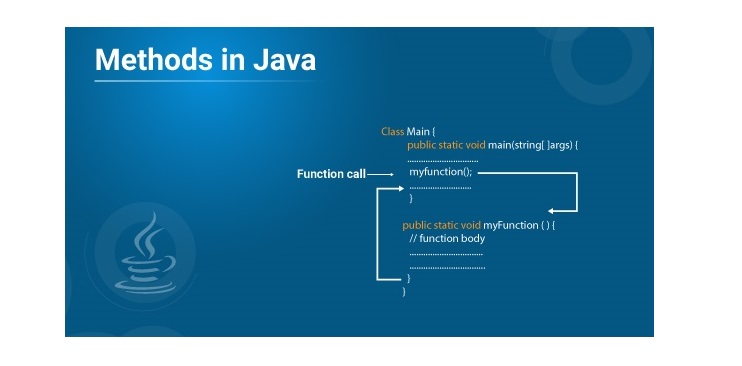
Method Type 1: User-Defined Methods
User-Defined nonstatic methods can be called or accessed only with the help of an instance of the class.
Syntax:
<ClassName> object=new <ClassName>
object.<MethodName>
Example
// Java Program to Illustrate User-Defined Methods
// Importing essential input output classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
class GFG {
// Method 1
// Method of this class
void hello()
{
// Print statement whenever this method s called
System.out.println("This is the userDefinedMethod");
}
// Method 2
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating instance of the class
// inside the main() method
GFG ob = new GFG();
// Calling the method of class 1
// inside class 2
ob.hello();
}
}
Output
This is the userDefinedMethod
Method Type 2: Abstract Methods
These are the methods that are declared inside the abstract class without the implementation of the method of a particular signature or without signature. We cannot call it abstract methods. To create the instance of the abstract class ,we have to extend the abstract class. Abstract Methods are used when we have to use the one-way property of the method in different ways.
Example
// Java Program to Illustrate Abstract Methods
// Class 1
// Helper class acting as Abstract class
abstract class GFGhelp {
// Creating abstract method
abstract void check(String name);
}
// Class 2
// Main class extending to helper class
public class GFG extends GFGhelp {
// main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating the instance of the class
GFG ob = new GFG();
// Accessing the abstract method
ob.check("GFG");
}
// Extends the abstract method
@Override void check(String name)
{
System.out.println(name);
}
}
Output
GFG
Method Type 3: Predefined Methods
These are the methods that are already implemented in the java library or predefined and inherited by every java class. For example, consider every class in the java inherited object class that has various methods. hashcode() is one of the methods of the object class that is inherited by every class in Java
Example
// Java Program to Illustrate Predefined Methods
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating object of the class in
// main() method
GFG ob = new GFG();
// Print the hashcode using
// predefined hashCode() method
System.out.println(ob.hashCode());
}
}
Output
1023892928
Method Type 4: Static methods
Static methods are those methods that there is no need for an instance of the class to access.Basically, these methods are the class methods and every static methods are shared among all the instances equally.
Example
// Java Program to Illustrate Static Methods
// Importing input output classes
import java.io.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Method 1
// Static method
static void hello()
{
// Print statement
System.out.println("Hello");
}
// Method 2
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// calling the Method 1
// Accessing method
hello();
}
}
Hello
Source: geeksforgeeks.org



0 comments:
Post a Comment