Allow an object to alter its behavior when its internal state changes. The object will appear to change its class.
Participants
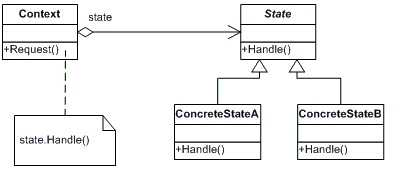
◉ Context: defines the interface of interest to clients Maintains an instance of a ConcreteState subclass that defines the current state.
◉ State: defines an interface for encapsulating the behavior associated with a particular state of the Context.
◉ Concrete State: each subclass implements a behavior associated with a state of Context
Code
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Context c = new Context(new ConcreteStateA());
c.request();
c.request();
c.request();
c.request();
}
}
public interface State {
void handle(Context context);
}
public class ConcreteStateA implements State {
@Override
public void handle(Context context) {
context.setState(new ConcreteStateB());
}
}
public class ConcreteStateB implements State {
@Override
public void handle(Context context) {
context.setState(new ConcreteStateA());
}
}
public class Context {
private State state;
public Context(State state) {
setState(state);
}
public State getState() {
return state;
}
public void setState(State state) {
this.state = state;
System.out.println("State: " + state.getClass().getSimpleName());
}
public void request() {
state.handle(this);
}
}
Output
State: ConcreteStateA
State: ConcreteStateB
State: ConcreteStateA
State: ConcreteStateB
State: ConcreteStateA




0 comments:
Post a Comment