Now we will see how to run and compile module program. Even if some of the commands look complex don’t worry, once you understand they will be easy and simple.
Before looking into how to run java modular program, let’s understand how to run java package program without using module-info.java file.
To separate out our source files and class files we will use ‘–d’ option to set the destination directory for class files.
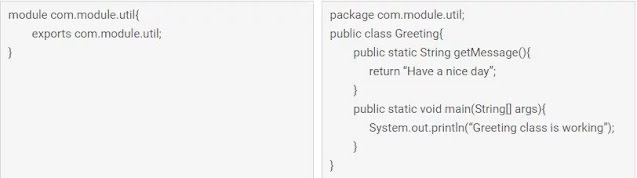
Let’s assume we want to run the above Greeting class which is present in the package ‘com.module.util’. And we will put the .class files under the ‘libs’ directory.
D:\project>javac -d libs com.module.util\com\module\util\Greeting.java
Once we execute the above command, we can see that the .class file is created under libs\com\module\util\Greeting.class
Now if we would like to run the main class created by above command, we have to specify path where jvm can find class files. Since our classes are present under libs folder we can specify path using –cp or -classpath.
D:\project>java -cp libs com.module.util.Greeting
OUTPUT
Greeting class is working
Compile and run java 9 module program
Now we have seen how to run java package program and put the classes into separate folder, to avoid mixing .java and .class files. We will use -d option for modular program as well.
Most important thing to remember is that, while compiling module, we have to compile .java source files and module descriptor file(module-info.java) .
In windows path are separated by semi-colon(;) and in Linux and mac using colons(:)
Most important new argument options
There are few new parameters/argument types introduced in java 9 for running the modular program that we must know.
1. module-path: Module-path option is used to specify where the modules are located. It is used at compile and run time.
- At compile time it is used with javac option to specify path where the dependent modules can be found.
Syntax : javac –module-path path1;path2
- At runtime it is used to specify dependent module and module which is to run
Syntax : java -module-path pathslist
Note: we can use -p path as shortcut for –module-path path.
2. module: The –module argument is used to compile list of modules or run a module.
- Syntax : javac –module path1;path2
- Syntax : java –module module/class
Note: we can use -m as shortcut for –module.
3. module-source-path: the argument –module-source-path us used to specify the root directory where the source files or packages are placed.
Sometimes the projects are organized in such a way that the code is placed in special folder.
For example src/main/java
Note: when we are using –module or –m option it is mandatory to use –module-source-path option, even if the source files are in same folder.
– – module-path == > -p
– – module == > -m
Example
D:\project> javac -d libs –module-source-path ./ –module com.module.app
D:\project> java –module-path libs –module com.module.app/com.module.app.Main
OUTPUT
Have a nice day
Different ways to compile and run java modules
1) We can specify all the files separated by space in javac command:
Warning: If you are using this option don’t compile multiple modules in same folder. Otherwise it will override module-info.class files
Syntax to compile:
javac –d outputDir --module-path requiredModulesPath moduleDir\module-info.java moduleDir\package\File1.java moduleDir\package1\package2\File2.java
java --module-path paths --module module/package.MainClass
Note: even in windows in java ‘/’ is used as separator for module and class
Example to compile com.module.util module
D:\project> javac -d libs com.module.util\com\module\util\Greeting.java com.module.util\module-info.java
After this command we should see module-info.class and Greeting.class files are created
project
├───libs
│ │ module-info.class
│ └───com
│ └───module
│ └───util
│ Greeting.class
Now we can run and check our module using following command
D:\project> java --module-path libs --module com.module.util/com.module.util.Greeting
Greeting class is working
Now lets run the Main class from app module which is dependent on util module which is compiled in libs path.
D:\project> javac --module-path libs -d app com.module.app\com\module\app\Main.java com.module.app\module-info.java
D:\project>java –module-path app;libs –module com.module.app/com.module.app.Main
Have a nice day
2) We can specify module names instead of java files:
This is recommended option to compile the applications. If we use this option, we can compile multiple modules in single directory as separate folder for each module with module name is created.
Also if required modules are in the same folder, they are automatically compiled even if they are not specified
Syntax to compile:
javac –d outputDir --module-path requiredModulesPath --module-source-path rootOfSOurceFiles --module modulesToBeCompiles
D:\project>javac -d libs --module-source-path ./ --module com.module.util,com.module.app
After executing above command, following classes are created
project
├───libs
│ ├───com.module.app
│ │ │ module-info.class
│ │ └───com
│ │ └───module
│ │ └───app
│ │ Main.class
│ └───com.module.util
│ │ module-info.class
│ └───com
│ └───module
│ └───util
│ Greeting.class
java --module-path requiredModulesPath --module module/package.MainClass
D:\project>java --module-path libs --module com.module.app/com.module.app.Main
Common mistakes in running modules
Let’s assume we would like to run Main class from com.module.app module.
Com.module.app module is dependent on com.module.util module.
Com.module.util module is compiled in libs folder
Com.module.app module is compiled in app folder.
When required modules is not specified in module path
java --module-path app -m com.module.app/com.module.app.Main
Error java.lang.module.FindException: Module com.module.util not found, required by com.module.app
When module path of the module which is to be run is not specified in module path
java --module-path libs-m com.module.app/com.module.app.Main
Error: java.lang.module.FindException Module com.module.app not found
When we use the wrong slash(\) to run –correct way is module/class
java --module-path libs;app -m com.module.app\com.module.app.Main
Fast track reading
◉ module-path: used to specify where the modules are located
◉ module: used to specify modules list for compile or module to run
◉ module-source-path: used to specify the root directroy where the source files or packages are places
◉ If we use –-module or –m option it is mandatory to use –-module-source-path option
◉ short codes -p can be used for –-module-path and -m for –module
◉ Syntax to compile javac –d outputDir -p requiredModulesPath –module-source-path rootOfSOurceFiles -m modulesToBeCompiles
◉ Run syntax: java -p requiredModulesPath -m module/package.MainClass
Frequently asked question FAQ:
What is Module resolution process?
When we run the module program, at start jvm checks for all required modules. This process of finding all modules at start is call as Module resolution process.
We can print modules scanning process log by using command –-show-module-resolution in the run command.
Note: in module resolution process first main module is searched then it keep adding required module in tree form.
What are the java restricted keyword or contextual keyword?
Newly added 10 keywords, which are considered as keyword only in case of Module descriptor file(module-info.java), are called as restricted keywords.
This keywords are open, module, requires, transitive, exports, opens, to, uses, provides, and with.
For backward compatibility in every other cases it is considered as identifiers. Unlike other keywords we can use this keywords is variables or method name.
What is module descriptor file?
From java 9, special file with name module-info.java is requied in root folder of module, which specifies the metadata of module, this file is called as module desciptor file.
Can we export multiple package in one line?
No, To export multiple packages separate exports keyword is required.
Can we add multiple modules dependancy using single requries keyword?
No for separate module new requires keyword is required.




0 comments:
Post a Comment