Cross-site scripting (XSS) is a type of security vulnerability in web applications where an attacker injects malicious scripts through some kind of user input (like input boxes, URL parameters, HTML headers, etc)
It is important to prevent XSS attacks to safeguard the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the information of the web application. The two main cross-site scripting flaws are reflected and stored:
Reflected XSS
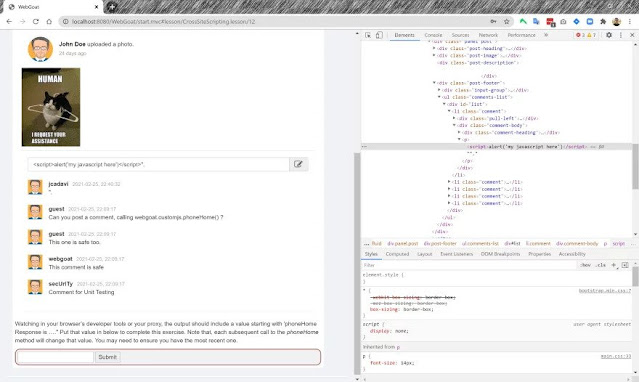
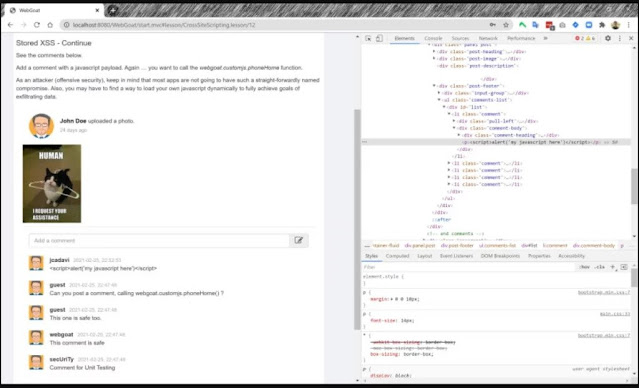
Malicious content from a user request is displayed to the user or it is written into the page after from server response. For instance, in the next screenshot, the credit card number field is vulnerable. After the number, there is a script to be injected:
<script src="data:text/javascript;base64,YWxlcnQoJ215IGphdmFzY3JpcHQgaGVyZScp" defer=""></script>








0 comments:
Post a Comment