This is a little bit of experimentation that I did recently to figure out a reasonable code to get all possible permutations of a set of characters.
So say given a set of characters “ABC”, my objective is to come up code which can spit out “ABC”, “ACB”, “BAC”, “BCA”, “CBA”, “CAB”.
The approach I took is to go with the definition of permutation itself, so with “ABCD” as the set of characters a 4 slot that needs to be filled.
The first slot can be filled by any of A, B, C, D, in 4 ways:
The second slot by any of the remaining 3 characters, so with “A” in the first slot –
The third slot by the remaining 2 characters, so with “A”, “B” in the first two slots:
And finally, the fourth slot by the remaining 1 character, with say “A”, “B”, “C” in the first 3 slots:
In total, there would be 4 for the first slot * 3 for the 2nd slot * 2 for the 3rd slot * 1 for the 4th slot – 24 permutations altogether.
I can do this in place, using an algorithm that looks like this:
package org.bk.algo.general;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
public class Permutations {
public List<string> permutations(String str) {
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
List<string> result = new ArrayList<>();
permutations(0, chars, result);
return result;
}
private void permutations(int idx, char[] arr, List<string> result) {
if (idx == arr.length - 1) {
result.add(new String(arr));
}
for (int i = idx; i <= arr.length - 1; i++) {
swap(arr, i, idx);
permutations(idx + 1, arr, result);
swap(arr, i, idx);
}
}
private void swap(char[] arr, int p1, int p2) {
if (p1 == p2) return;
char temp = arr[p1];
arr[p1] = arr[p2];
arr[p2] = temp;
}
@Test
void testPerms() {
List<string> abcdPerms = permutations("ABCD");
assertThat(abcdPerms).hasSize(24);
assertThat(abcdPerms)
.containsExactlyInAnyOrder(
"ABCD", "ABDC", "ACBD", "ACDB", "ADCB", "ADBC", "BACD", "BADC", "BCAD", "BCDA", "BDCA", "BDAC",
"CBAD", "CBDA", "CABD", "CADB", "CDAB", "CDBA", "DBCA", "DBAC", "DCBA", "DCAB", "DACB", "DABC");
}
}
</string></string></string></string>
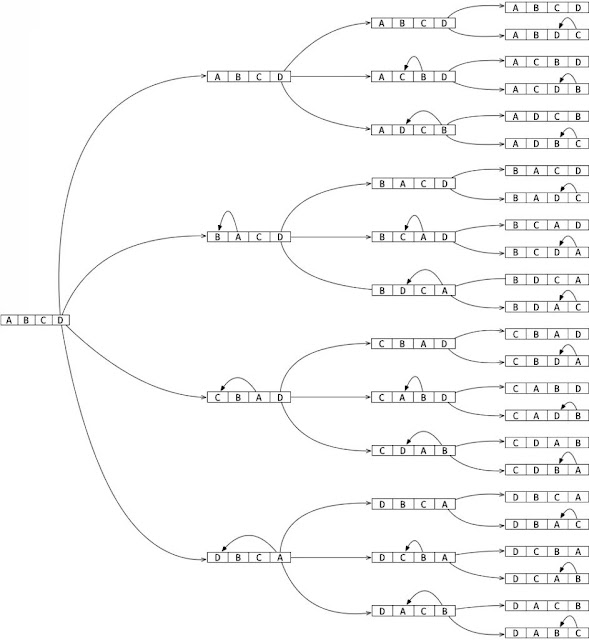
A trace of flow and the swaps is here:
The only trick here is that the code does all the holding of characters and getting it into the right place in place by swapping the right characters to the right place and restoring it at the end of it.
This works well for a reasonably sized set of characters – reasonable because for just 10 characters, there would be 3,628,800 permutations.
An algorithm that works even better, though a complete mystery to me how it actually functions, is the Heap’s Algorithm. Here is a java implementation of it:
package org.bk.algo.general;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
public class PermutationsHeap {
public List<string> permutations(String str) {
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
List<string> result = new ArrayList<>();
permutations(chars.length, chars, result);
return result;
}
private void permutations(int k, char[] arr, List<string> result) {
if (k == 1) {
result.add(new String(arr));
return;
}
permutations(k - 1, arr, result);
for (int i = 0; i < k - 1; i++) {
if (k % 2 == 0) {
swap(arr, i, k - 1);
} else {
swap(arr, 0, k - 1);
}
permutations(k - 1, arr, result);
}
}
private void swap(char[] arr, int p1, int p2) {
if (p1 == p2) return;
char temp = arr[p1];
arr[p1] = arr[p2];
arr[p2] = temp;
}
@Test
void testPerms() {
List<string> abcdPerms = permutations("ABCD");
assertThat(abcdPerms).hasSize(24);
assertThat(abcdPerms)
.containsExactlyInAnyOrder(
"ABCD", "ABDC", "ACBD", "ACDB", "ADCB", "ADBC", "BACD", "BADC", "BCAD", "BCDA", "BDCA", "BDAC",
"CBAD", "CBDA", "CABD", "CADB", "CDAB", "CDBA", "DBCA", "DBAC", "DCBA", "DCAB", "DACB", "DABC");
}
}
</string></string></string></string>
It very efficiently does one swap per permutation, which is still high but better than the approach that I have described before.
In a sample perumutation of 8 characters, which generates 40320 permutations, the home cooked version swaps 80638 times, and the Heap’s algorithm swaps 40319 times! thus proving its efficacy.






0 comments:
Post a Comment