In this post, we will see how we can create AWS Lambda function in Java and I tell you, it is quite easy to do so…
Basically, there are three ways in which we can create AWS Lambda function :
– By implementing RequestHandler interface
– By implementing RequestStreamHandler interface
– Custom implementation, which does not require us to implement any AWS specific interface
Basically, there are three ways in which we can create AWS Lambda function :
– By implementing RequestHandler interface
– By implementing RequestStreamHandler interface
– Custom implementation, which does not require us to implement any AWS specific interface
AWS Lambda function by implementing RequestHandler interface
For using this method of creating AWS lambda function, we need to have following dependency in our project :
<dependency>
<groupId>com.amazonaws</groupId>
<artifactId>aws-lambda-java-core</artifactId>
<version>1.1.0</version>
</dependency>
And below is how your class will look like :
package com.blogspot.javasolutionsguide;
import com.amazonaws.services.lambda.runtime.Context;
import com.amazonaws.services.lambda.runtime.RequestHandler;
public class HelloWorldWithRequestHandler implements RequestHandler<object,object> {
@Override
public Object handleRequest(Object input, Context context) {
return String.format("Hello %s%s.", input ," from " + context.getFunctionName());
}
}
</object,object>
Once you have created maven project with above dependency and class in your project, maven build the project, which will create jar for you in the target folder of your project.
Now open the AWS Console, go to Services and search for AWS Lambda.
On the following screen ,click on Create Function.
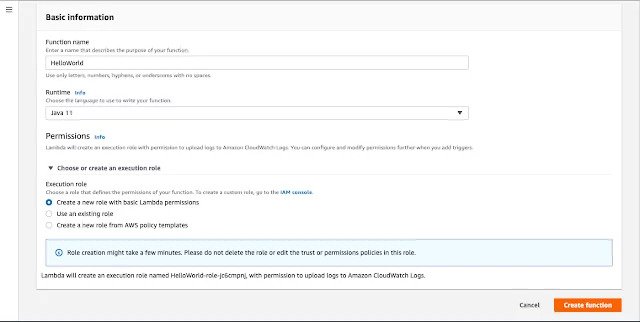
On following screen, enter Function name “HelloWorld” and choose Runtime as Java 11.
In Permissions section, choose “Create a new role with basic Lambda permissions”and AWS Lambda will create and execution role with name HelloWorld-role-jc6cmpnj. This role is required to allow AWS Lambda to upload logs to AWS Cloudwatch logs.
Click on Create Function.
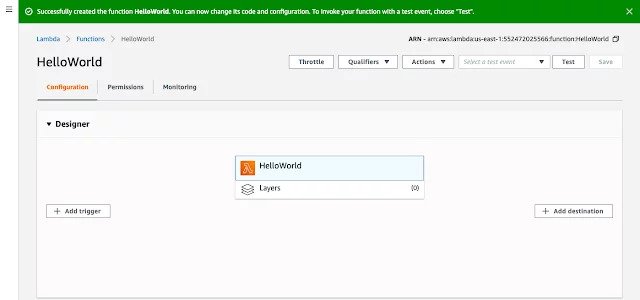
You will see following screen, where it says that “Successfully created the function HelloWorld.You can now change its code and configuration.To invoke your function with a test event, choose Test”.
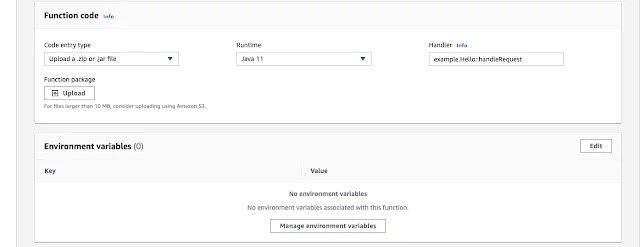
Now in the Function code section, click on the upload button and browse on your computer for the jar that you created earlier.
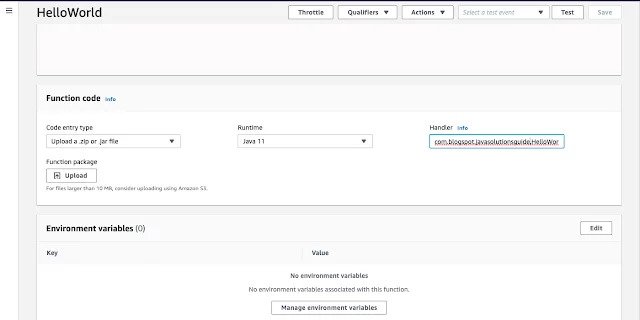
– Also, in the Handler textbox, replace
example with package name where your “HelloWorldWithRequestHandler” class is residing, which in our case it is “
com.blogspot.javasolutionsguide“
– And replace Hello with “HelloWorldWithRequestHandler”.
– And replace handleRequest will stays as is ,because we also have same method name in our class.
Click on Save button on extreme right side of the screen.
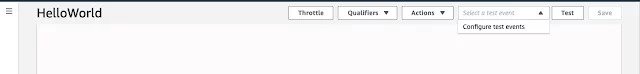
Now to test our lambda function, we need to configure test event(s),for which we will click on “Select a Test event” drop down and then click on “Configure test events”.
You will see following screen.Enter Event name as “HelloWorldEvents” and replace following
{
“key1”: “value1”,
“key2”: “value2”,
“key3”: “value3”
}
with just your name like as below :
“Gaurav Bhardwaj”
and click on Create button.
Now click on Test button and you should see your lambda function executed successfully with message “Hello Gaurav Bhardwaj from HelloWorld”,which is the output returned by our lambda function.
If you click on the logs link in the above screen, it will take you to the AWS Cloudwatch screen where you can see that for your lambda function a LogGroup has been created and under which you have LogStream where you can see logs of your lambda function.This was the reason we assigned role to our lambda function, because AWS lambda used that role to push logs to the Cloudwatch.
AWS Lambda function by implementing RequestStreamHandler interface
In this case you need to follow exact same steps as in above case.It is just that in the code you need to implement RequestStreamHandler interface rather than RequestHandler interface as below.
package com.blogspot.javasolutionsguide;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import com.amazonaws.services.lambda.runtime.Context;
import com.amazonaws.services.lambda.runtime.RequestStreamHandler;
public class HelloWorldWithRequestStreamHandler implements RequestStreamHandler {
@Override
public void handleRequest(InputStream inputStream, OutputStream outputStream, Context context) throws IOException {
int letter;
while((letter = inputStream.read()) != -1)
{
outputStream.write(Character.toUpperCase(letter));
}
}
}
AWS Lambda function by custom implementation, which does not require us to implement any AWS specific interface
You can also have your custom lambda function ,which does not follow signature from some AWS specific interface.You can even omit Context object as well, if you don’t want it.
In the following code,I have tried to put two handler methods, one with Context object and one without Context object.To test these both ,you just need to change the name of the method in the AWS console and it will start hitting that method.
Also ,we can see that from Context object ,we can get lots of useful information like name of AWS fucnton,its version,ARN,how much memory is allocated to the function(by default it is 512 mb) .
package com.blogspot.javasolutionsguide;
import com.amazonaws.services.lambda.runtime.Context;
public class HelloWorld {
//Handler method without Context
public String sayHelloWorldWithoutContext(String name) {
return String.format("Hello %s.", name);
}
//We need to add aws-lambda-java-core dependency if we add Context as parameter.
public String sayHelloWorldWithContext(String name, Context context) {
context.getLogger().log("Lambda Function Name:" + context.getFunctionName() +
"Version:" + context.getFunctionVersion() +
"Arn:" + context.getInvokedFunctionArn() +
"Allocated Memory:" + context.getMemoryLimitInMB() +
"Remaining Time:"+ context.getRemainingTimeInMillis());
return String.format("Hello %s.", name);
}
}
Also in the following example ,we can see that if we have two handler methods with same name in our class,the handler method which has Context object as its last parameter will be called.
package com.blogspot.javasolutionsguide;
import com.amazonaws.services.lambda.runtime.Context;
public class HelloWorldWithMultipleHandlersWithSameName {
public String handler(String name) {
return String.format("Hello %s.", name);
}
public String handler(String name, Context context) {
return String.format("Hello %s%s.", name, " Memory Allocated:" + context.getMemoryLimitInMB());
}
}










0 comments:
Post a Comment